Architecture and Design¶
We’ll start with the C4 views:
Context
Container – this isn’t too interesting, but it can help to see this.
Components
This is a collection of various design notes describing some implementation details.
The code view is in the API Reference section.
Context¶
There are two distinct contexts for CEL Python:
The CLI – as a stand-alone application.
As an importable module to provide expressions to a DSL.
![@startuml
skinparam actorStyle awesome
left to right direction
package celpy {
package library {
usecase lib1 as "extend DSL with expressions"
usecase lib2 as "create program"
usecase lib3 as "evaluate program in context"
lib1 --> lib2
lib1 --> lib3
}
package cli {
usecase cli1 as "**expr** features
---
Use the -n option"
usecase cli2 as "**test** features
---
Use the -nb options"
usecase cli3 as "**jq** features
Newline-Delimited or single JSON doc"
usecase cli4 as "interactive computation
---
use the -i option"
}
}
actor app as "some app with a DSL"
app --> lib1
actor bash as "shell script"
bash --> cli1
bash --> cli2
bash --> cli3
actor user
user --> cli4
app <|- [c7n]
@enduml](_images/plantuml-c970d97dc7e0a41eb7666fff5d466440fc8d67cf.png)
From the CLI, the celpy application has a number of use cases:
A shell script can use
celpyas a command to replace other shell commands, including expr, test, and jq.A person can run
celpyinteractively. This allows experimentation. It also supports exploring very complex JSON documents to understand their structure.
As a library, an application (for example, C7N) can import celpy to provide an expression feature for the DSL.
This provides well-defined semantics, and widely-used syntax for the expression language.
There’s an explicit separation between building a program and executing the program to allow caching an expression for multiple executions without the overhead of building a Lark parser or compiling the expression.
Container¶
As a CLI, this is part of a shell script. It runs where the script runs.
As a library, this is improted into the application to extend the DSL.
There are no services offered or used.
Components¶
The Python code base has a number of modules.
__init__– thecelpypackage as a whole.__main__– the main applications used when runningcelpy.celparser– a Facade for the Lark parser.evaluation– a Facade for run-time evaluation.celtypes– the underlying Python implementations of CEL data structures.c7nlib– a collection of components the C7N can use to introduce CEL filters.adapter– Some JSON serialization components.
Here’s the conceptual organiation
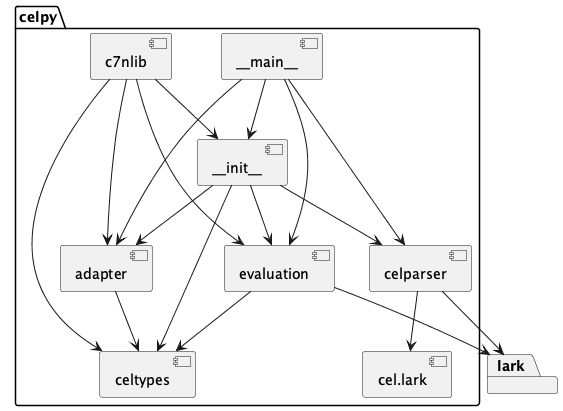
While there is a tangle of dependencies, there are three top-level “entry points” for celpy.
The
__main__module is the CLI application.The
c7nlibmodule exposes CEL functionality in a form usable by Cloud Custodian filter definitions. This library provides useful components to perform Custodian-related computations.The
__init__module is exposes the most useful parts ofcelpyfor integration woth another application.
Compile-Time¶
Here are the essential classes used to compile a CEL expression and prepare it for evaluation.
![@startuml
hide empty members
class Environment {
package: str
annotations: dict[str, Annotation]
compile(text: str) -> lark.Tree
program(expr: lark.Tree, functions: dict) -> Runner
}
class celparser.CELParser{
parse(text: str)
}
Environment *-- CELParser
class lark.Tree {}
CELParser --> lark.Tree : "Creates"
abstract class Runner {
ast: Tree
evaluate(context: Context) -> Value
}
Environment --> Runner : "Creates"
Runner o-- lark.Tree
Runner o-- "0..m" CELFunction
class InterpretedRunner
Runner <|-- InterpretedRunner
class evaluation.Evaluator
InterpretedRunner *-- Evaluator
class CompiledRunner
Runner <|-- CompiledRunner
class evaluation.Transpiler
CompiledRunner *-- Transpiler
class evaluation.Context << (T,orchid) Type>> {
key: str
value: Result | NameContainer
}
Runner o--- "0..m" Context
class CELFunction <<Callable>>
class Annotation << (T,orchid) Type>>
Environment o-- "0..m" Annotation
class TypeType
Annotation <|-- TypeType
Annotation <|-- CELFunction
@enduml](_images/plantuml-60c95188891b5d1267db67bb61a17e9fd7c08060.png)
The fundamental sequence of operations is
Create an
celpy.Environmentwith any neededcelpy.Annotationinstances. For the most part, these are based on the overall application domain. Any type definitions should be subclasses ofcelpy.TypeTypeor a callable function defined by thecelpy.CELFunctiontype.Use the
celpy.Environmentto compile the CEL text to create a parse tree.Use the
celpy.Environmentto create acelpy.Runnerinstance from the parse tree and any function definitions that override or extend the predefined CEL environment.Evaluate the
celpy.Runnerwith acelpy.Context. Thecelpy.Contextprovides specific values for variables required for evaluation. Generally, each variable should have ancelpy.Annotationdefined in thecelpy.Environment.
The celpy.Runner can be evaluated with any number of distinct celpy.Context values.
This amortizes the cost of compilation over multiple executions.
Evaluation-Time¶
Here’s the classes to evaluate a CEL expression.
![@startuml
hide empty members
abstract class Runner {
ast: Tree
evaluate(context: Context) -> Value
}
Environment --- Runner : "Created By <"
Runner o-- "0..m" CELFunction
Runner o-- Context
class lark.Tree
Tree --* Runner
class InterpretedRunner <<Adapter>>
Runner <|-- InterpretedRunner
abstract class lark.Interpreter
class evaluation.Evaluator {
activation: Activation
functions: dict[str, CELFunction]
evaluate() -> Value
}
lark.Interpreter <|--- Evaluator
InterpretedRunner *-- Evaluator
class CompiledRunner <<Adapter>>
Runner <|-- CompiledRunner
InterpretedRunner -[hidden]> CompiledRunner
class evaluation.Transpiler {
functions: dict[str, CELFunction]
transpile()
evaluate() -> Value
}
CompiledRunner *-- Transpiler
lark.Interpreter <|--- Transpiler
class evaluation.Activation {
annotations: Annotation
identifiers: dict[str, Result | CELFunction]
}
Runner *-- Activation : "Uses"
Runner --> Activation : "Creates"
Activation --> Activation : "based on"
class Annotation << (T,orchid) Type>>
Runner *-- "0..m" Annotation
Annotation --o Activation : Initializes
CELFunction --o Activation : Initializes
Context --o Activation : Initializes
@enduml](_images/plantuml-165a23eb11f806bdd308ffac47a78125152ade58.png)
The evalation of the CEL expression is done via a celpy.Runner object.
There are two celpy.Runner implementations.
The
celpy.InterpretedRunnerwalks the AST, creating the final resultcelpy.Valueorcelpy.CELEvalErrorexception. This uses acelpy.evaluation.Activationto perform the evaluation.The
celpy.CompiledRunnertranspiles the AST into a Python sequence of statements. The internalcompile()creates a code object that can then be evaluated with a givencelpy.evaluation.ActivationThe internalexec()functions performs the evaluation.
The subclasses of celpy.Runner are Adapter classes to provide a tidy interface to the somewhat more complex celpy.Evaluator or celpy.Transpiler objects.
In the case of the celpy.InterpretedRunner, evaluation involves creating an celpy.evaluation.Activation and visiting the AST.
Whereas, the celpy.CompiledRunner must first visit the AST to create code. At evaluation time, it create an celpy.evaluation.Activation and uses exec() to compute the final value.
The celpy.evaluation.Activation contains several things:
The
Annotationdefinitions to provide type information for identifiers.The
CELFunctionfunctions that extend or override the built-in functions.The values for identifiers.
The celpy.evaluation.Activation is a kind of chainmap for name resolution.
The chain has the following structure:
The end of the chain has the built-in defaults. (This is the bottom-most base definition.)
A layer on top of this can offer types and functions which are provided to integrate into the containing app or framework.
The next layer is the “current” activation when evaluating a given expression. For the CLI, this has the command-line variables. For other integrations, these are the input values.
A transient layer on top of this is used to create a local variable binding for the macro evaluations. These can be nested, and introduce the macro variable as a temporary annotation and value binding.
CEL Types¶
There are ten extension types that wrap Python built-in types to provide the unique CEL semantics.
celtypes.TypeTypeis a supertype for CEL types.celtypes.BoolTypewrapsintand creates additional type overload exceptions.celtypes.BytesTypewrapsbytesit handles conversion fromceltypes.StringType.celtypes.DoubleTypewrapsfloatand creates additional type overload exceptions.celtypes.IntTypewrapsintand adds a 64-bit signed range constraint.celtypes.UintTypewrapsintand adds a 64-bit unsigned range constraint.celtypes.ListTypewrapslistand includes some type overload exceptions.celtypes.MapTypewrapsdictand includes some type overload exceptions. Additionally, theMapKeyTypestype hint is the subset of types permitted as keys.celtypes.StringTypewrapsstrand includes some type overload exceptions.celtypes.TimestampTypewrapsdatetime.datetimeand includes a number of conversions fromdatetime.datetime,int, andstrvalues.celtypes.DurationTypewrapsdatetime.timedeltaand includes a number of conversions fromdatetime.timedelta,int, andstrvalues.
Additionally, a celtypes.NullType is defined, but does not seem to be needed. It hasn’t been deleted, yet.
It should be considered deprecated.
Transpiler Missing Names¶
The member_dot transpilation with a missing name will be found at evaluation time via member.get('IDENT'). This raises No Such Member in Mapping error.
The primary :: ident evaluation can result in one of the following conditions:
identdenotes a type definition. The value’s type isTypeType. The value is a type referenceboolbecomescelpy.celtypes.BoolType.
identdenotes a built-in function. The value’s type isCELFunction. The value is the Python function reference.
identdenotes an annotation, but the value’s type is neitherTypeTypenorCELFunction.The transpiled value is
f"activation.{ident}", assuming it will be a defined variable.If, at
exec()time the name is not in the Activation with a value, aNameErrorexception will be raised that becomes aCELEvalErrorexception.
The Member-Dot Production¶
Consider protobuf_message{field: 42}.field.
This is parsed using the following productions.
member : member_dot | member_dot_arg | member_item | member_object | primary
member_dot : member "." IDENT
member_object : member "{" [fieldinits] "}"
The member_object will be a primary which can be an ident.
It MUST refer to the Annotation (not the value) because it has fieldinits.
All other choices are (generally) values.
They can be annotations, which means bool.type() works the same as type(bool).
Here’s primary production, which defines the ident in the member production.
primary : dot_ident_arg | dot_ident | ident_arg | ident
| paren_expr | list_lit | map_lit | literal
The ident is not always transpiled as activation.{name}.
Inside member_object, it’s activation.resolve_name({name}).
Outside member_object, it can be activation.{name} because it’s a simple variable.
It may make sense to rename the Activation.resolve_name() method to Activation.get().
This, however, overloads the get() method.
This has type hint consequences.
Important
The member can be any of a variety of objects:
NameContainer(Dict[str, Referent])ActivationMapType(Dict[Value, Value])MessageType(MapType)
All of these classes must define a get() method.
The nuance is the NameContainer is also a Python dict and there’s an
overload issue between that get() and other get() definitions.
The Transpilation currently leverages a common method named get() for all of these types.
This is a Pythonic approach, but, the overload for the NameContainer (a Dict subclass) isn’t quite right:
it doesn’t return a Referent, but the value from a Referent.
A slightly smarter approach is to define a get_value(member, 'name') function that uses a match/case structure to do the right thing for each type. The problem is, the result is a union of type, value, function, and any of these four containers!
Another possibility is to leverage the Annotations. They can provide needed type information to discern which method with specific result type.